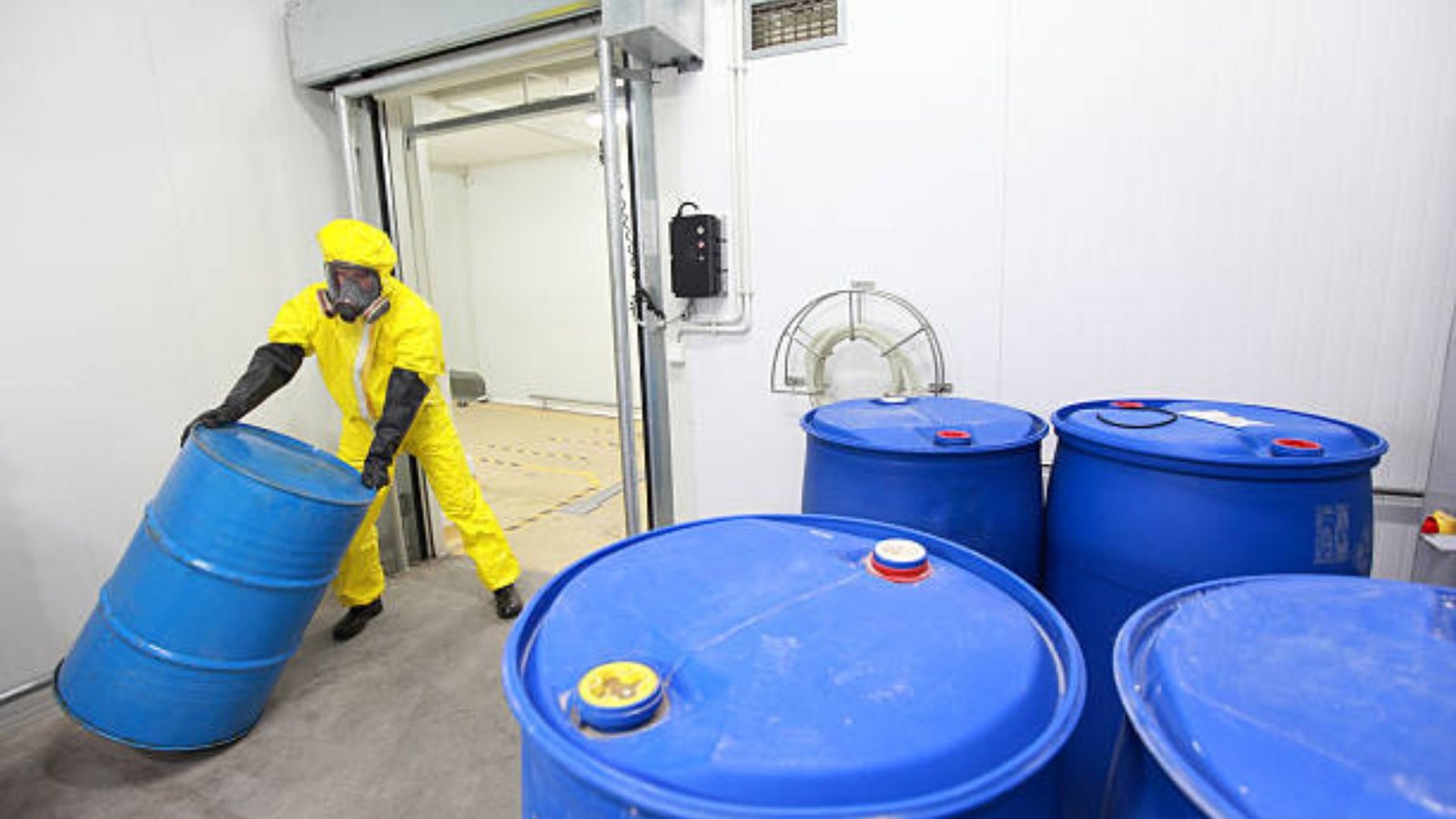
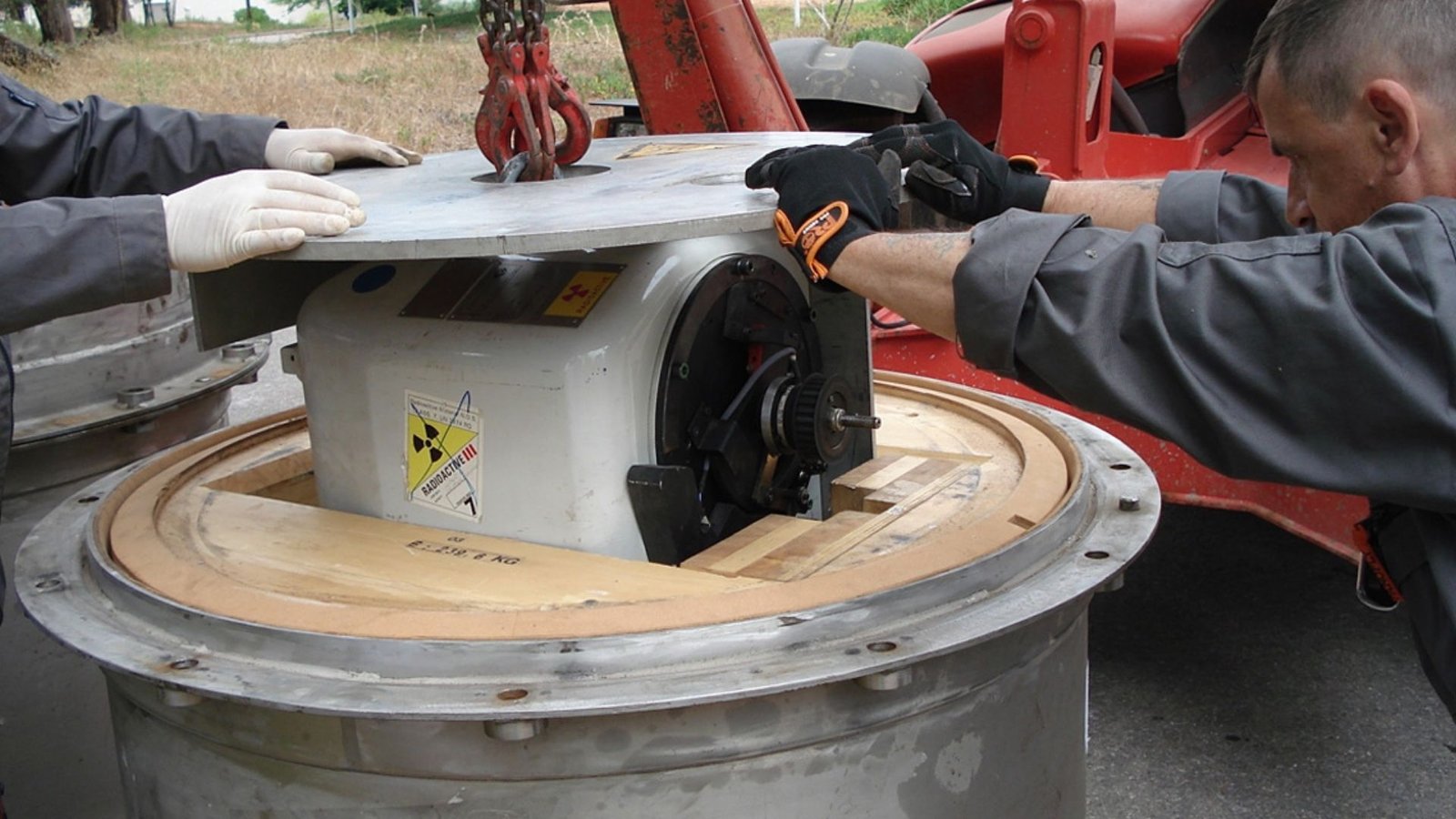
Radioactive waste management is a critical issue that requires careful planning and execution. As society continues to use nuclear technology for energy, medicine, and research, the safe storage of radioactive waste becomes increasingly important. In this post, we will explore safe storage solutions for radioactive waste, highlighting methods that protect both the environment and public safety.
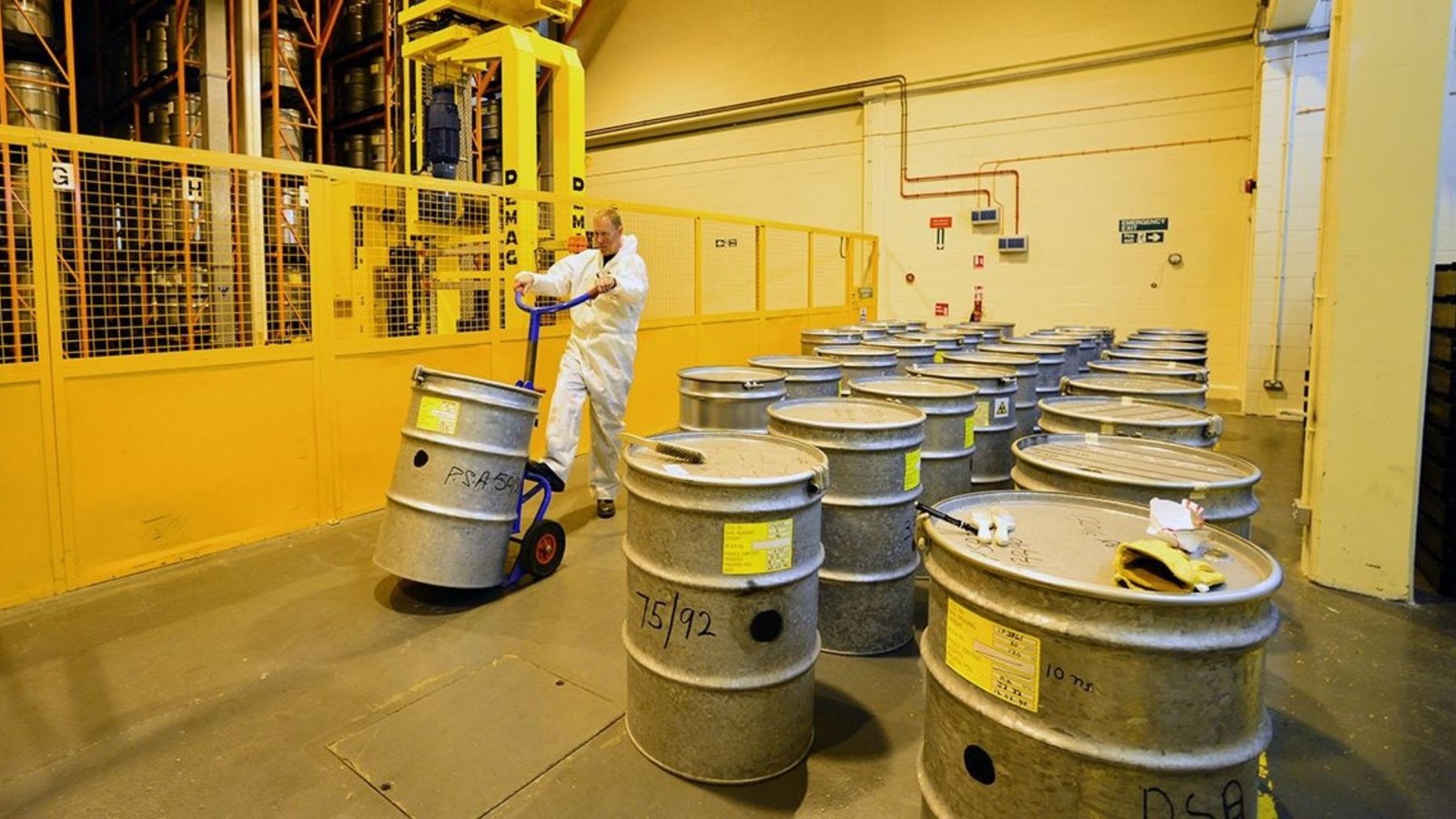

The Importance of Safe Storage
Radioactive waste can remain hazardous for thousands of years, making its safe storage essential. Improper storage can lead to contamination of land, water, and air, posing serious health risks to humans and wildlife. Therefore, implementing robust storage solutions is crucial to ensure that radioactive materials are contained and monitored effectively.
Types of Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste is classified into several categories based on its origin and level of radioactivity:
- Low-Level Waste (LLW): This includes items like clothing, tools, and medical equipment that have been contaminated with small amounts of radioactivity.
- Intermediate-Level Waste (ILW): This waste generates a significant amount of heat and includes materials such as reactor components and chemical sludges.
- High-Level Waste (HLW): Primarily produced from nuclear reactors, HLW is highly radioactive and generates a large amount of heat. It requires specialized handling and storage solutions.
Safe Storage Solutions
1. Deep Geological Repositories
Deep geological repositories are considered one of the safest long-term storage solutions for high-level radioactive waste. These facilities are located deep underground in stable geological formations, which provide natural barriers against radiation. By isolating waste from the environment, these repositories significantly reduce the risk of contamination.
2. Dry Cask Storage
Dry cask storage is another effective method for managing spent nuclear fuel. After cooling in a pool for several years, spent fuel is placed in steel and concrete casks. These casks are designed to shield against radiation and protect against environmental factors. Dry cask storage is a viable option for both interim and long-term management.
3. Vault Storage
Vault storage is used primarily for intermediate-level waste. This method involves storing waste in heavily shielded buildings or vaults that provide both physical protection and radiation containment. These facilities are engineered to withstand potential natural disasters, ensuring that the waste remains secure.
4. Encapsulation
Encapsulation involves sealing radioactive waste in durable materials, such as glass or concrete, to prevent the release of radiation. This method is often used for high-level waste and ensures that the materials remain stable over long periods. Encapsulation is crucial for transportation and long-term storage solutions.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Safe storage solutions also require ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure their effectiveness. Regular inspections and monitoring systems help detect any potential leaks or structural issues. Additionally, maintaining accurate records of waste inventory and storage conditions is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
Regulatory Framework
Safe storage of radioactive waste is governed by strict regulations and guidelines set by national and international agencies. Organizations such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) provide frameworks for the safe management of radioactive materials. Compliance with these regulations is critical for ensuring public safety and environmental protection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding safe storage solutions for radioactive waste is vital for protecting public health and the environment. From deep geological repositories and dry cask storage to vault storage and encapsulation, these methods provide effective means of managing radioactive materials. Continuous monitoring and adherence to regulatory standards further enhance safety. As we advance in nuclear technology, prioritizing safe storage solutions is essential for a sustainable future. Let’s commit to responsible management practices that ensure the safe handling of radioactive waste!