Handling radioactive waste is a serious responsibility. To protect public health and the environment, there are strict regulatory guidelines in place. These guidelines help ensure that radioactive waste is managed safely from its creation to its final disposal. In this blog post, we will explore the key regulations and regulatory guidelines for handling radioactive waste safely.
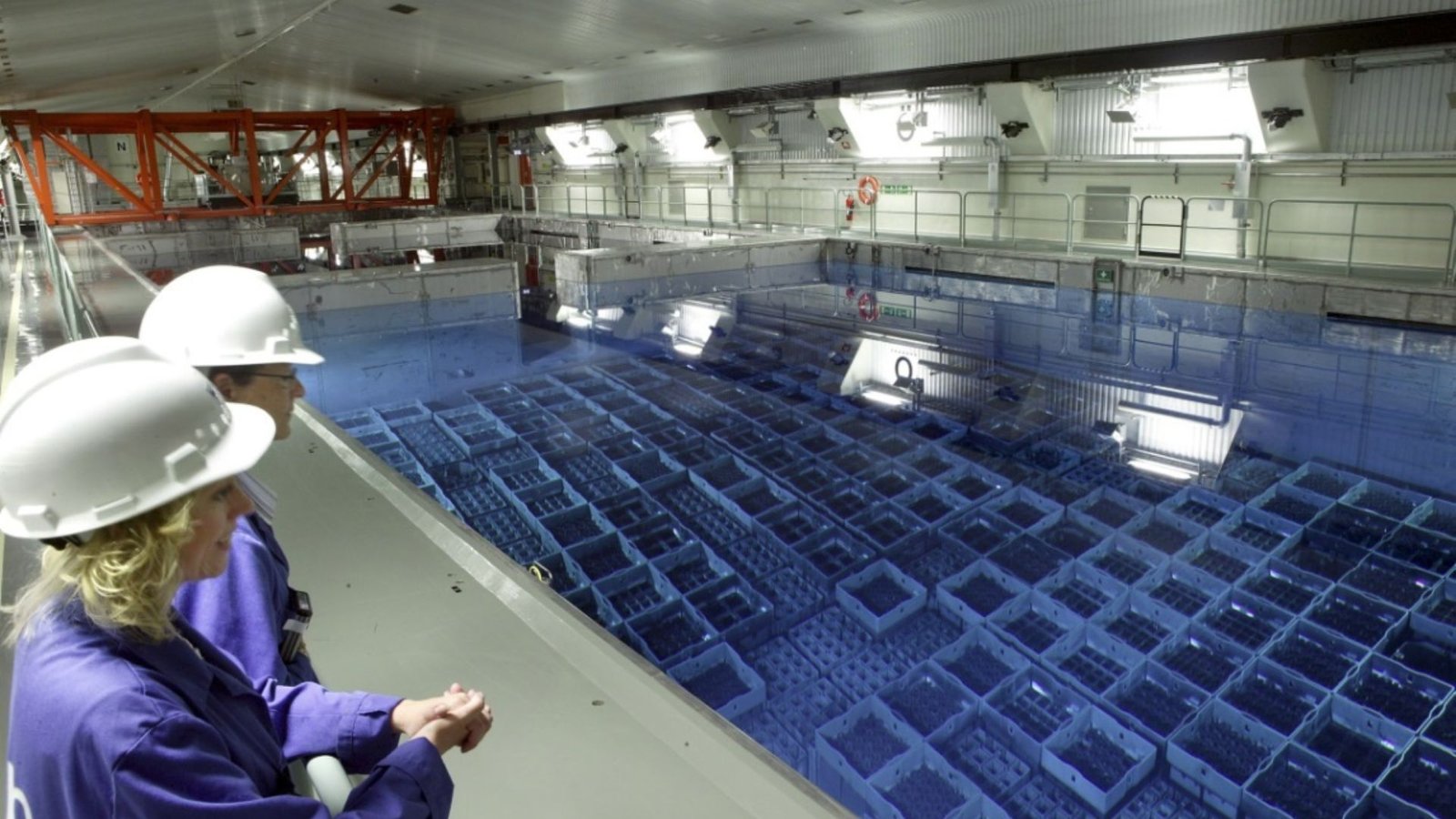

Understanding Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory guidelines for radioactive waste are established by various agencies. In the United States, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is a key organization overseeing nuclear safety. Similarly, international bodies like the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) set global standards.
These agencies create rules to manage radioactive waste safely. They cover everything from waste classification to disposal methods. Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone involved in handling radioactive materials.
Waste Classification
One of the first steps in managing radioactive waste is classification. Waste is categorized based on its level of radioactivity. Generally, there are three main categories:
- High-Level Waste (HLW): This includes spent nuclear fuel and other highly radioactive materials.
- Intermediate-Level Waste (ILW): This type contains some radioactivity but can be handled with less stringent measures.
- Low-Level Waste (LLW): This includes items like contaminated clothing or equipment, which have lower levels of radioactivity.
Each category has specific handling and disposal requirements outlined by regulatory guidelines.
Safe Storage Practices
Regulatory guidelines emphasize the importance of safe storage practices. Radioactive waste must be stored in designated facilities that meet safety standards. These facilities are designed to prevent leaks and contain radiation.
For example, high-level waste is often stored in deep geological repositories, while low-level waste may be kept in above-ground facilities. Regular inspections and monitoring are essential to ensure these storage sites remain secure.
Transportation Regulations
Transporting radioactive waste requires strict adherence to safety protocols. Regulations govern how waste should be packaged and labeled during transport. Containers must be robust and designed to prevent leaks or radiation exposure.
Additionally, transport routes are carefully planned to minimize risk to the public. Agencies often require detailed plans for emergency response in case of accidents during transport.
Disposal Methods
Disposal of radioactive waste is one of the most critical aspects of waste management. Regulatory guidelines dictate acceptable disposal methods based on waste classification.
- High-Level Waste: Typically disposed of in deep geological formations that can isolate it from the environment for thousands of years.
- Intermediate-Level Waste: This may be disposed of in surface facilities or deep geological sites, depending on its specific characteristics.
- Low-Level Waste: Often disposed of in near-surface landfills designed to contain the waste safely.
Following these guidelines helps prevent harmful exposure to radiation and protects the environment.
Public Involvement and Transparency
Regulatory guidelines also emphasize the importance of public involvement and transparency. Communities living near radioactive waste sites should be informed about potential risks and safety measures.
Public hearings and consultations allow community members to express concerns and ask questions. This engagement helps build trust and ensures that regulations consider the needs and opinions of residents.
Continuous Training and Education
To comply with regulatory guidelines, continuous training and education for personnel handling radioactive waste are essential. Workers must be knowledgeable about safety protocols, waste handling procedures, and emergency response plans.
Regulatory agencies often require regular training sessions to ensure that staff stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and best practices. This commitment to education helps reduce accidents and enhance overall safety.
Conclusion: Commitment to Safety
In conclusion, regulatory guidelines for handling radioactive waste are vital for protecting public health and the environment. By following these regulations—ranging from waste classification to disposal methods—we can ensure that radioactive materials are managed safely.
It is essential for all stakeholders, including government agencies, industries, and communities, to work together in this effort. By prioritizing safety and compliance, we can create a safer future for everyone. Let’s commit to responsible radioactive waste management and protect our planet.